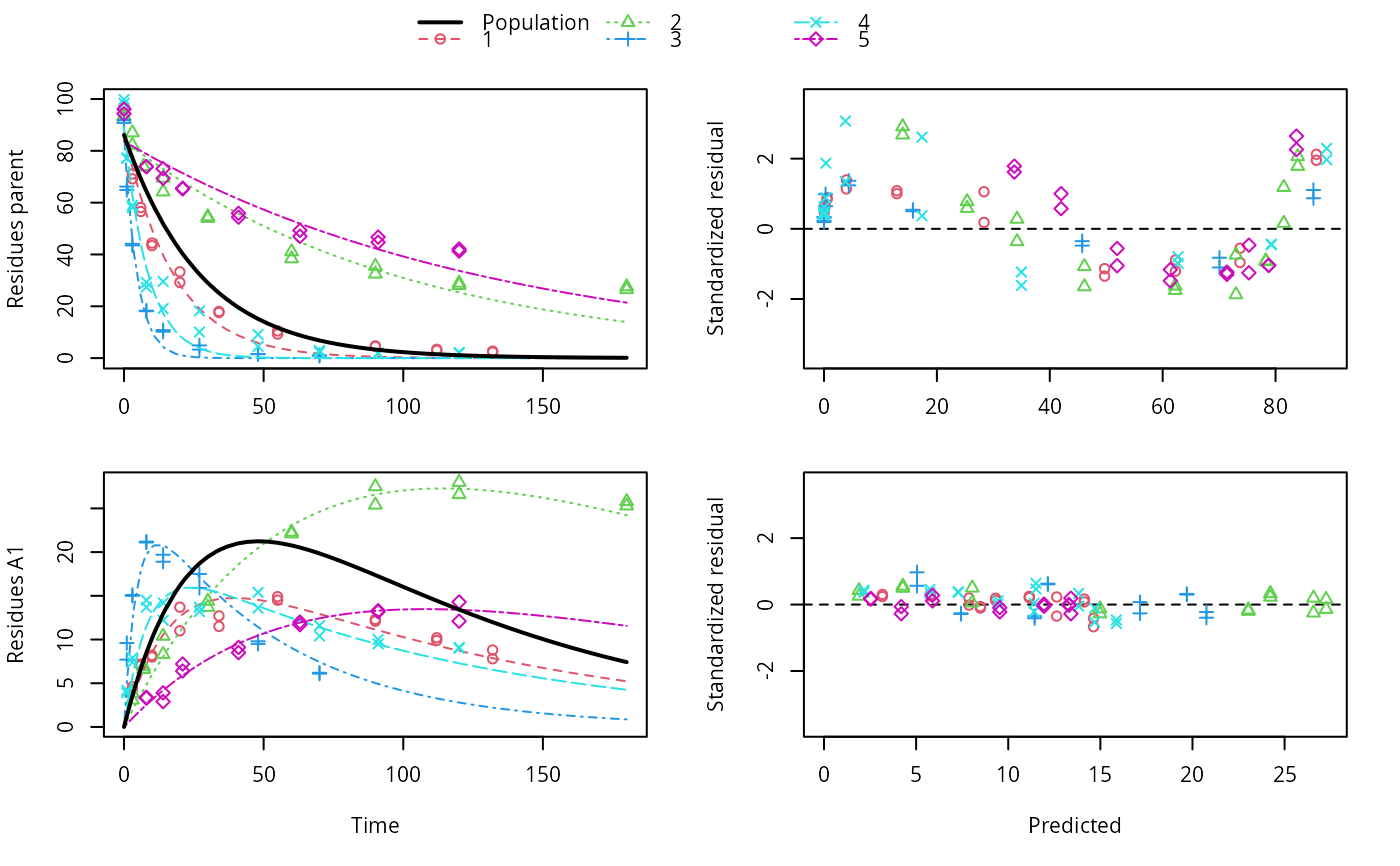This functions sets up a nonlinear mixed effects model for an mmkin row object. An mmkin row object is essentially a list of mkinfit objects that have been obtained by fitting the same model to a list of datasets.
# S3 method for mmkin nlme( model, data = sys.frame(sys.parent()), fixed, random = fixed, groups, start, correlation = NULL, weights = NULL, subset, method = c("ML", "REML"), na.action = na.fail, naPattern, control = list(), verbose = FALSE ) # S3 method for nlme.mmkin print(x, ...) # S3 method for nlme.mmkin update(object, ...)
Arguments
| model | An mmkin row object. |
|---|---|
| data | Ignored, data are taken from the mmkin model |
| fixed | Ignored, all degradation parameters fitted in the mmkin model are used as fixed parameters |
| random | If not specified, all fixed effects are complemented with uncorrelated random effects |
| groups | See the documentation of nlme |
| start | If not specified, mean values of the fitted degradation parameters taken from the mmkin object are used |
| correlation | See the documentation of nlme |
| weights | passed to nlme |
| subset | passed to nlme |
| method | passed to nlme |
| na.action | passed to nlme |
| naPattern | passed to nlme |
| control | passed to nlme |
| verbose | passed to nlme |
| x | An nlme.mmkin object to print |
| ... | Update specifications passed to update.nlme |
| object | An nlme.mmkin object to update |
Value
Upon success, a fitted 'nlme.mmkin' object, which is an nlme object with additional elements. It also inherits from 'mixed.mmkin'.
Note
As the object inherits from nlme::nlme, there is a wealth of
methods that will automatically work on 'nlme.mmkin' objects, such as
nlme::intervals(), nlme::anova.lme() and nlme::coef.lme().
See also
nlme_function(), plot.mixed.mmkin, summary.nlme.mmkin,
parms.nlme.mmkin
Examples
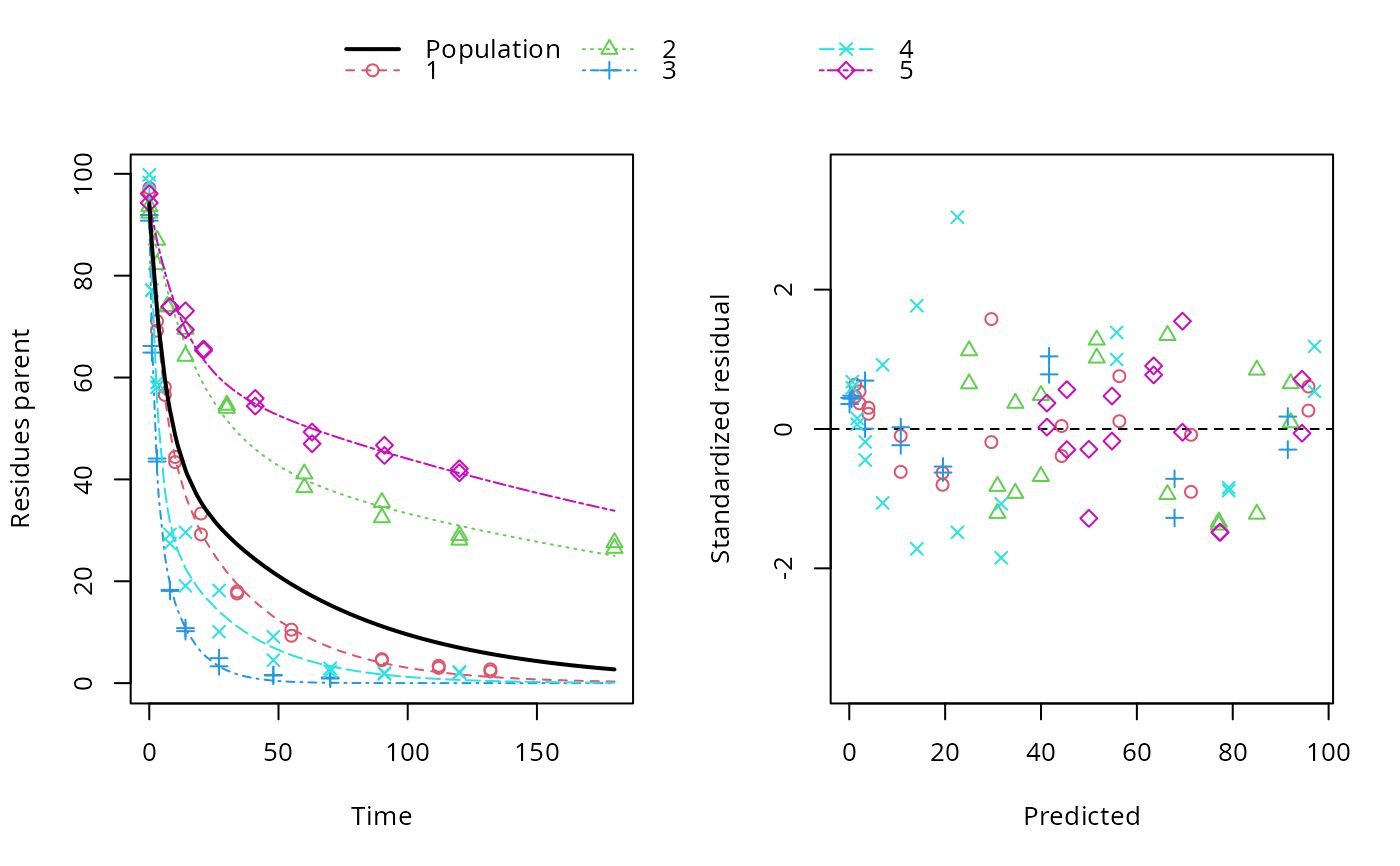
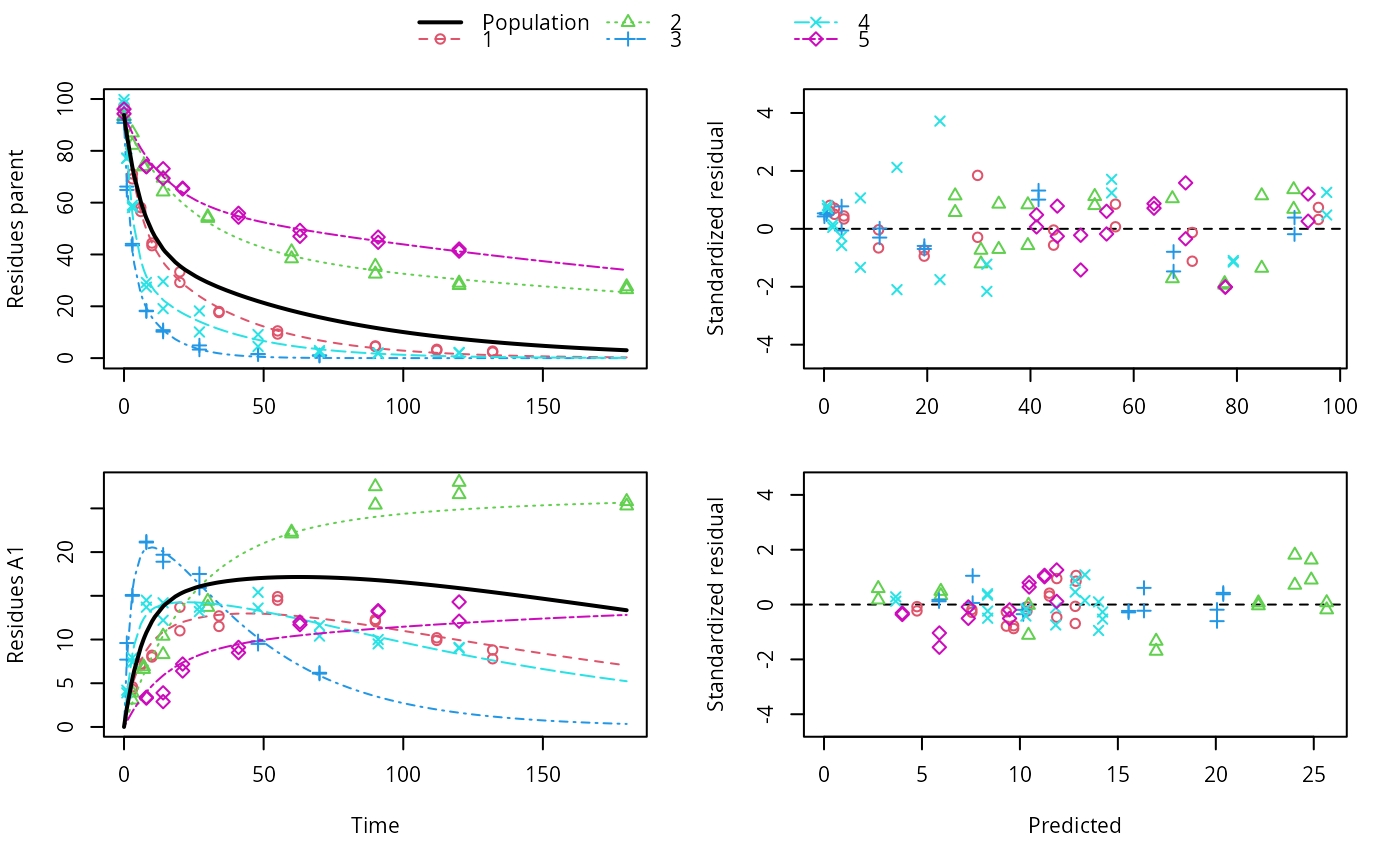
ds <- lapply(experimental_data_for_UBA_2019[6:10], function(x) subset(x$data[c("name", "time", "value")], name == "parent")) f <- mmkin(c("SFO", "DFOP"), ds, quiet = TRUE, cores = 1) library(nlme) f_nlme_sfo <- nlme(f["SFO", ]) f_nlme_dfop <- nlme(f["DFOP", ]) AIC(f_nlme_sfo, f_nlme_dfop)#> df AIC #> f_nlme_sfo 5 625.0539 #> f_nlme_dfop 9 495.1270#> Kinetic nonlinear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood #> #> Structural model: #> d_parent/dt = - ((k1 * g * exp(-k1 * time) + k2 * (1 - g) * exp(-k2 * #> time)) / (g * exp(-k1 * time) + (1 - g) * exp(-k2 * time))) #> * parent #> #> Data: #> 90 observations of 1 variable(s) grouped in 5 datasets #> #> Log-likelihood: -238.5635 #> #> Fixed effects: #> list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k1 ~ 1, log_k2 ~ 1, g_qlogis ~ 1) #> parent_0 log_k1 log_k2 g_qlogis #> 94.17015185 -1.80015278 -4.14738834 0.03239833 #> #> Random effects: #> Formula: list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k1 ~ 1, log_k2 ~ 1, g_qlogis ~ 1) #> Level: ds #> Structure: Diagonal #> parent_0 log_k1 log_k2 g_qlogis Residual #> StdDev: 2.488249 0.8447275 1.32965 0.4651789 2.321364 #>#> $distimes #> DT50 DT90 DT50back DT50_k1 DT50_k2 #> parent 10.79857 100.7937 30.34192 4.193937 43.85442 #># \dontrun{ f_nlme_2 <- nlme(f["SFO", ], start = c(parent_0 = 100, log_k_parent = 0.1)) update(f_nlme_2, random = parent_0 ~ 1)#> Kinetic nonlinear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood #> #> Structural model: #> d_parent/dt = - k_parent * parent #> #> Data: #> observations of 0 variable(s) grouped in 0 datasets #> #> Log-likelihood: -404.3729 #> #> Fixed effects: #> list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k_parent ~ 1) #> parent_0 log_k_parent #> 75.933480 -3.555983 #> #> Random effects: #> Formula: parent_0 ~ 1 | ds #> parent_0 Residual #> StdDev: 0.002416792 21.63027 #>ds_2 <- lapply(experimental_data_for_UBA_2019[6:10], function(x) x$data[c("name", "time", "value")]) m_sfo_sfo <- mkinmod(parent = mkinsub("SFO", "A1"), A1 = mkinsub("SFO"), use_of_ff = "min", quiet = TRUE) m_sfo_sfo_ff <- mkinmod(parent = mkinsub("SFO", "A1"), A1 = mkinsub("SFO"), use_of_ff = "max", quiet = TRUE) m_dfop_sfo <- mkinmod(parent = mkinsub("DFOP", "A1"), A1 = mkinsub("SFO"), quiet = TRUE) f_2 <- mmkin(list("SFO-SFO" = m_sfo_sfo, "SFO-SFO-ff" = m_sfo_sfo_ff, "DFOP-SFO" = m_dfop_sfo), ds_2, quiet = TRUE) f_nlme_sfo_sfo <- nlme(f_2["SFO-SFO", ]) plot(f_nlme_sfo_sfo)# For the following fit we need to increase pnlsMaxIter and the tolerance # to get convergence f_nlme_dfop_sfo <- nlme(f_2["DFOP-SFO", ], control = list(pnlsMaxIter = 120, tolerance = 5e-4), verbose = TRUE)#> #> **Iteration 1 #> LME step: Loglik: -404.9583, nlminb iterations: 1 #> reStruct parameters: #> ds1 ds2 ds3 ds4 ds5 ds6 #> -0.4114356 0.9798646 1.3524300 0.7293315 0.3354323 1.3647313 #> Beginning PNLS step: .. completed fit_nlme() step. #> PNLS step: RSS = 630.3633 #> fixed effects: 93.82269 -5.455993 -0.9601037 -1.862196 -4.199671 0.07824609 #> iterations: 120 #> Convergence crit. (must all become <= tolerance = 0.0005): #> fixed reStruct #> 0.7897284 0.5822782 #> #> **Iteration 2 #> LME step: Loglik: -407.7755, nlminb iterations: 11 #> reStruct parameters: #> ds1 ds2 ds3 ds4 ds5 ds6 #> -0.37122411 0.00305562 1.44336560 0.72467122 0.30160310 1.40762692 #> Beginning PNLS step: .. completed fit_nlme() step. #> PNLS step: RSS = 630.3637 #> fixed effects: 93.82269 -5.455992 -0.9601036 -1.862196 -4.199671 0.0782462 #> iterations: 120 #> Convergence crit. (must all become <= tolerance = 0.0005): #> fixed reStruct #> 1.375673e-06 9.758294e-06#> Model df AIC BIC logLik Test L.Ratio p-value #> f_nlme_dfop_sfo 1 13 843.8547 884.6201 -408.9274 #> f_nlme_sfo_sfo 2 9 1085.1821 1113.4043 -533.5910 1 vs 2 249.3274 <.0001#> $ff #> parent_sink parent_A1 A1_sink #> 0.5912432 0.4087568 1.0000000 #> #> $distimes #> DT50 DT90 #> parent 19.13518 63.5657 #> A1 66.02155 219.3189 #>#> $ff #> parent_A1 parent_sink #> 0.2768574 0.7231426 #> #> $distimes #> DT50 DT90 DT50back DT50_k1 DT50_k2 #> parent 11.07091 104.6320 31.49738 4.462384 46.20825 #> A1 162.30523 539.1663 NA NA NA #>if (length(findFunction("varConstProp")) > 0) { # tc error model for nlme available # Attempts to fit metabolite kinetics with the tc error model are possible, # but need tweeking of control values and sometimes do not converge f_tc <- mmkin(c("SFO", "DFOP"), ds, quiet = TRUE, error_model = "tc") f_nlme_sfo_tc <- nlme(f_tc["SFO", ]) f_nlme_dfop_tc <- nlme(f_tc["DFOP", ]) AIC(f_nlme_sfo, f_nlme_sfo_tc, f_nlme_dfop, f_nlme_dfop_tc) print(f_nlme_dfop_tc) }#> Kinetic nonlinear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood #> #> Structural model: #> d_parent/dt = - ((k1 * g * exp(-k1 * time) + k2 * (1 - g) * exp(-k2 * #> time)) / (g * exp(-k1 * time) + (1 - g) * exp(-k2 * time))) #> * parent #> #> Data: #> 90 observations of 1 variable(s) grouped in 5 datasets #> #> Log-likelihood: -238.4298 #> #> Fixed effects: #> list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k1 ~ 1, log_k2 ~ 1, g_qlogis ~ 1) #> parent_0 log_k1 log_k2 g_qlogis #> 94.04774566 -1.82339808 -4.16715311 0.05685186 #> #> Random effects: #> Formula: list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k1 ~ 1, log_k2 ~ 1, g_qlogis ~ 1) #> Level: ds #> Structure: Diagonal #> parent_0 log_k1 log_k2 g_qlogis Residual #> StdDev: 2.473881 0.8499884 1.337185 0.4659005 1 #> #> Variance function: #> Structure: Constant plus proportion of variance covariate #> Formula: ~fitted(.) #> Parameter estimates: #> const prop #> 2.23224114 0.01262341f_2_obs <- mmkin(list("SFO-SFO" = m_sfo_sfo, "DFOP-SFO" = m_dfop_sfo), ds_2, quiet = TRUE, error_model = "obs") f_nlme_sfo_sfo_obs <- nlme(f_2_obs["SFO-SFO", ]) print(f_nlme_sfo_sfo_obs)#> Kinetic nonlinear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood #> #> Structural model: #> d_parent/dt = - k_parent_sink * parent - k_parent_A1 * parent #> d_A1/dt = + k_parent_A1 * parent - k_A1_sink * A1 #> #> Data: #> 170 observations of 2 variable(s) grouped in 5 datasets #> #> Log-likelihood: -472.976 #> #> Fixed effects: #> list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k_parent_sink ~ 1, log_k_parent_A1 ~ 1, log_k_A1_sink ~ 1) #> parent_0 log_k_parent_sink log_k_parent_A1 log_k_A1_sink #> 87.975536 -3.669816 -4.164127 -4.645073 #> #> Random effects: #> Formula: list(parent_0 ~ 1, log_k_parent_sink ~ 1, log_k_parent_A1 ~ 1, log_k_A1_sink ~ 1) #> Level: ds #> Structure: Diagonal #> parent_0 log_k_parent_sink log_k_parent_A1 log_k_A1_sink Residual #> StdDev: 3.992214 1.77702 1.054733 0.4821383 6.482585 #> #> Variance function: #> Structure: Different standard deviations per stratum #> Formula: ~1 | name #> Parameter estimates: #> parent A1 #> 1.0000000 0.2050003# The same with DFOP-SFO does not converge, apparently the variances of # parent and A1 are too similar in this case, so that the model is # overparameterised #f_nlme_dfop_sfo_obs <- nlme(f_2_obs["DFOP-SFO", ], control = list(maxIter = 100)) # }